IB Approaches to Learning
-
Through ATL in IB programmes, students develop skills that have relevance across the curriculum that help them “learn how to learn.”
ATL skills can be learned and taught, improved with practice, and developed incrementally. They provide a solid foundation for learning independently and with others. ATL skills help students prepare for, and demonstrate learning through, meaningful assessment. They provide a common language that students and teachers can use to reflect on, and articulate on, the process of learning.
IB programmes identify five ATL skill categories, expanded into developmentally appropriate skill clusters.
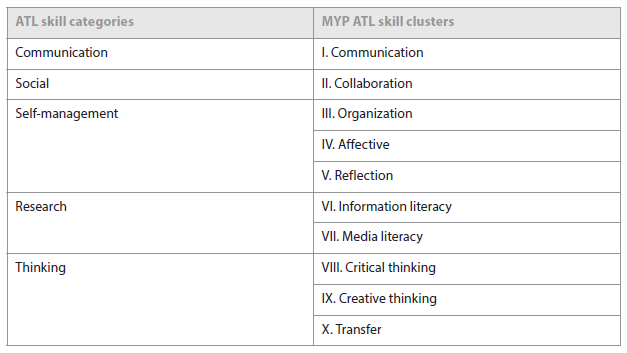
All teachers in IB schools are responsible for integrating and explicitly teaching ATL skills.
Over time, students should develop clear and sophisticated understandings of how they learn best and how they can evaluate the effectiveness of their learning. This kind of self-regulated (independent and autonomous) learning helps students:- reflect purposefully on their learning (metacognition)
- understand the diversity of human learning needs
- evaluate and provide evidence of their learning
- meet MYP subject group aims and objectives
- share responsibility for creating productive, cooperative, and safe learning environments
- develop the confidence to try new strategies and explore new concepts and contexts for learning
- prepare for further study and responsible participation in local and global communities.
ATL skills are informed by, and support the development of, the attributes of the IB learner profile.







